Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iriya, Keishiro*; *; Fujita, Hideki*; Kubo, Hiroshi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-034, 212 Pages, 2000/02
Cementious materials and highly compacted bentnite are expectable candidates as materials of TRU waste repositories. It was pointed out that Bentonite might be changed to Zeolite and surrounding rock might be altered by high alkalinity water flow, since cement hydrate leached to pore water of cement and it was changed to alkaline. Transportation of radio-nuclides might be accelerated by organic materials, such as super plasticizer, and nitlate which is contained in nuclear wastes. It was concluded by previous studies that rock and bentonite is stable in alkaline water which pH is less than 10.5. The new type of low alkalinity cement with high silica fume and fly ash content which could keep pH below 11.0 was developed and its performance has been assessed. However since Zeolitation and ilitation were reported upon deterioration of bentonite bated in certain condition, it should be assessed by long term experiment. Since Capacity of keeping integrity of bentonite hasn't been directly checked by experiments upon the developed new type of low alkalinity cement it should be done. Although amount of leaching organic was quantitatively and experimentally assessed at an early age, effect of changing of amount and shape hasn't assessed in leaching of radio nuclides. Although it is pointed out that deterioration of cementitious materials isn't accelerated by condensed nitrate solution at early period after closure, it is considered that it might be accelerated corresponding to chemical composition in case of decrement of concentration of nitrate. In this study, deterioration of materials will be assessed in detail in order to feed back the results to assessment of transportation of radio nuclides. Long term deterioration of bentonite by leaching water of cement will be experimentally assessed, and deteriorating test of bentonite will be carried out by leaching water of low alkalinity cement. Amount of organic and component of it will be measured. Furthermore ...
Iriya, Keishiro*; *; Kubo, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Hideki*
JNC TJ8400 2000-033, 95 Pages, 2000/02
Cementious materials and highly compacted bentnite are expectable candidates as materials of TRU waste repositories. It was pointed out that Bentonite might be changed to Zeolite and surrounding rock might be altered by high alkalinity water flow, since cement hydrate leached to pore water of cement and it was changed to alkaline. Transportation of radio-nuclides might be accelerated by organic materials, such as super plasticizer, and nitrate which is contained in nuclear wastes. It was concluded by previous studies that rock and bentonite is stable in alkaline water which pH is less than 10.5. The new type of low alkalinity cement with high silica fume and fly ash content which could keep pH below 11.0 was developed and its performance has been assessed. However since Zeolitation and ilitation were reported upon deterioration of bentonite bated in certain condition, it should be assessed by long term experiment. Since Capacity of keeping integrity of bentonite hasn't been directly checked by experiments upon the developed new type of low alkalinity cement it should be done. Although amount of leaching organic was quantitatively and experimentally assessed at an early age, effect of changing of amount and shape hasn't assessed in leaching of radio nuclides. Although it is pointed out that deterioration of cementitious materials isn't accelerated by condensed nitrate solution at early period after closure, it is considered that it might be accelerated corresponding to chemical composition in case of decrement of concentration of nitrate. In this study, deterioration of materials will be assessed in detail in order to feed back the results to assessment of transportation of radio nuclides. Long term deterioration of bentonite by leaching water of cement will be experimentally assessed, and deteriorating test of bentonite will be carried out by leaching water of low alkalinity cement. Amount of organic and component of it will be measured. Furthermore ...
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
There has been a strong motivation to develop new cation exchange membranes suitable for the Bunsen reaction in the thermochemical water splitting IS process. We prepared cation exchange membranes by a radiation grafting polymerization method. The grafting reaction into a poly(ethylene-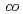 -tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The grafted membrane showed two times lower water permeation flux and three times higher activation energy of water diffusion than Nafion212 though both the membranes exhibited a similar water uptake. Therefore, the DVB-based crosslinking in the graft polymer would restrict water permeation through the membrane.
-tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The grafted membrane showed two times lower water permeation flux and three times higher activation energy of water diffusion than Nafion212 though both the membranes exhibited a similar water uptake. Therefore, the DVB-based crosslinking in the graft polymer would restrict water permeation through the membrane.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Sawada, Shinichi; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
A thermochemical water-splitting IS process, known to be one of the hydrogen production methods, includes the Bunsen reaction, SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI. Researchers previously attempted the Bunsen reaction using a Nafion membrane in an electrochemical cell and then found SO
+ 2HI. Researchers previously attempted the Bunsen reaction using a Nafion membrane in an electrochemical cell and then found SO permeation through the membrane problematic. Therefore, our research target is to develop Nafion-alternative cation exchange membranes for applications in the electrochemical Bunsen reaction by radiation-graft polymerization. In an effort to do so, we report here the design of a new grafting container, which enables us to prepare large-size membranes for up-scaling the IS process. The stainless-steel reactor had more or less volumetric capacity than the conventional separable glass container. In designing such a vessel, there were two important issues to be considered: (1) how to heat a grafting solution fast and uniformly and (2) how to situate substrate films in the container.
permeation through the membrane problematic. Therefore, our research target is to develop Nafion-alternative cation exchange membranes for applications in the electrochemical Bunsen reaction by radiation-graft polymerization. In an effort to do so, we report here the design of a new grafting container, which enables us to prepare large-size membranes for up-scaling the IS process. The stainless-steel reactor had more or less volumetric capacity than the conventional separable glass container. In designing such a vessel, there were two important issues to be considered: (1) how to heat a grafting solution fast and uniformly and (2) how to situate substrate films in the container.
 -ray irradiation graft polymerization method
-ray irradiation graft polymerization methodGoto, Mitsuaki*; Omori, Masayuki*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Sawada, Shinichi; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Kitamura, Akane; Higa, Mitsuru*
no journal, ,
We have prepared cation exchange membranes for applications to electrochemical energy-conversion devices by swift-heavy-ion irradiation, and then investigated their charge density,  , a concentration of fixed charge groups, in comparison with that of the conventional
, a concentration of fixed charge groups, in comparison with that of the conventional  -ray-grafted membranes. Poly(ethylene-
-ray-grafted membranes. Poly(ethylene-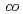 -tetrafluoroethylene) films with a 25
-tetrafluoroethylene) films with a 25  m thickness were irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m thickness were irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe and subsequently immersed in a grafting solution containing sodium
Xe and subsequently immersed in a grafting solution containing sodium  -styrenesulfonate at 60
-styrenesulfonate at 60 C. The charge density was estimated through the measurement of the membrane potential in an aqueous solution of potassium chloride. Our membranes exhibited higher charge density (reaching 2.40 mol/dm
C. The charge density was estimated through the measurement of the membrane potential in an aqueous solution of potassium chloride. Our membranes exhibited higher charge density (reaching 2.40 mol/dm at maximum) than the
at maximum) than the  -ray-grafted samples probably due to track structures characteristic of the bombarding heavy ions.
-ray-grafted samples probably due to track structures characteristic of the bombarding heavy ions.
Goto, Mitsuaki*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Sawada, Shinichi; Kitamura, Akane; Higa, Mitsuru*
no journal, ,
We have exploited a grafting technique with heavy-ion beams to create ion exchange membranes for various practical applications such as fuel cells and water desalination systems. In this study, instead of styrene that is a common monomer, sodium styrene sulfonate (SSS) was for the first time employed for this so-called ion-track grafting. A 25  m-thick poly(vinylidene fluoride) film was bombarded with 560 MeV
m-thick poly(vinylidene fluoride) film was bombarded with 560 MeV  Xe at a fluence of 3.0
Xe at a fluence of 3.0 10
10 or 1.0
or 1.0 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm , and subsequently immersed in a SSS grafting solution at 60
, and subsequently immersed in a SSS grafting solution at 60 C. The charge density was estimated through the measurement of the membrane potential in an aqueous solution of potassium chloride. Our membranes exhibited higher charge density than the conventional or commercially-available samples probably due to track structures characteristic of the bombarding heavy ions.
C. The charge density was estimated through the measurement of the membrane potential in an aqueous solution of potassium chloride. Our membranes exhibited higher charge density than the conventional or commercially-available samples probably due to track structures characteristic of the bombarding heavy ions.